2022/7/16BsKeyToolsChainsTools绑定样条线大约 2 分钟
Chain Tools 链条工具
使用样条线创建骨骼链绑定,适用于制作尾巴、脊椎、触手、绳索等柔性结构。
✨ 功能概述
- 🔗 创建连接到样条线的骨骼链
- 🎯 支持 IK 拉伸控制
- 🔄 多种朝向约束方式
- ⚙️ 灵活的样条线控制选项
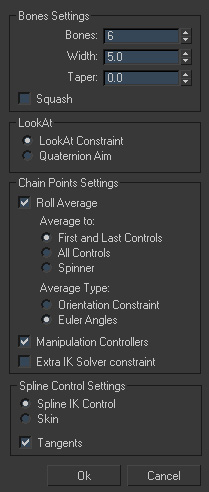
🦴 骨骼设置
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Bones | 链中创建的骨骼数量 |
| Width | 链骨的宽度 |
| Taper | 链骨的锥度 |
| Squash | 启用拉伸时的挤压效果 |
🎯 朝向方式 (LookAt)
骨骼朝向其目标(样条线上的辅助对象)的方式:
LookAt Constraint
- 使用标准的 LookAt 约束
- 以控制点助手作为目标
- 设置简单直观
Quaternion Aim
- 使用旋转脚本代替 LookAt 约束
- 通过四元数计算旋转值
- 优点:防止不必要的翻转
- 注意:骨骼与父级重叠时可能出现问题(X 轴方向相反)
📍 链点设置
链点是通过路径约束附加到样条线的辅助对象。
滚动平均值 (Roll Average)
链点的 X 旋转方向平均值设置:
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| First and Last Controls | 仅首尾控制点影响滚动 |
| All Controls | 所有控制点参与计算 |
| Spinner | 使用属性修改器中的滑块控制 |
平均类型 (Average Type)
| 类型 | 说明 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| Quat Constraint | 使用四元数计算 | 控制点有约束或非欧拉控制器 |
| Euler Angles | 使用欧拉角 X 轨迹计算 | 需要超过 180° 扭转且不翻转 |
欧拉角模式限制
使用欧拉角时,控制点不能分配除欧拉角以外的约束或旋转控制器
操纵控制器
勾选后为链点分配列表控制器,可独立编辑变换:
- 同时拥有位置约束和可编辑控制器
- 支持路径约束的同时进行手动调整
📏 IK 拉伸控制
Extra IK Solver Constraint
启用此选项可控制链的拉伸:
- 创建额外的样条线 IK 求解器
- 生成拉伸控制滑块
- 分配给控制点使用
🎛️ 样条线控制
定义样条线顶点的控制方式:
| 方式 | 说明 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| Spline IK Control | 使用样条线 IK 控制修改器 | 无法直接控制切线手柄,需通过控制点旋转 |
| Skin | 使用蒙皮修改器 | 可用助手控制切线手柄位置 |
| Tangents | 创建切线控制助手 | 需配合 Skin 方式使用 |
💡 使用建议
适用场景
- 🐍 尾巴、触手、蛇形生物
- 🦴 柔性脊椎
- 🔗 锁链、绳索
- 🌿 藤蔓、植物茎干
最佳实践
- 骨骼数量:根据需要的弯曲细节选择,一般 8-16 个
- 朝向方式:优先使用 Quaternion Aim 避免翻转
- 样条控制:需要控制切线时选择 Skin + Tangents